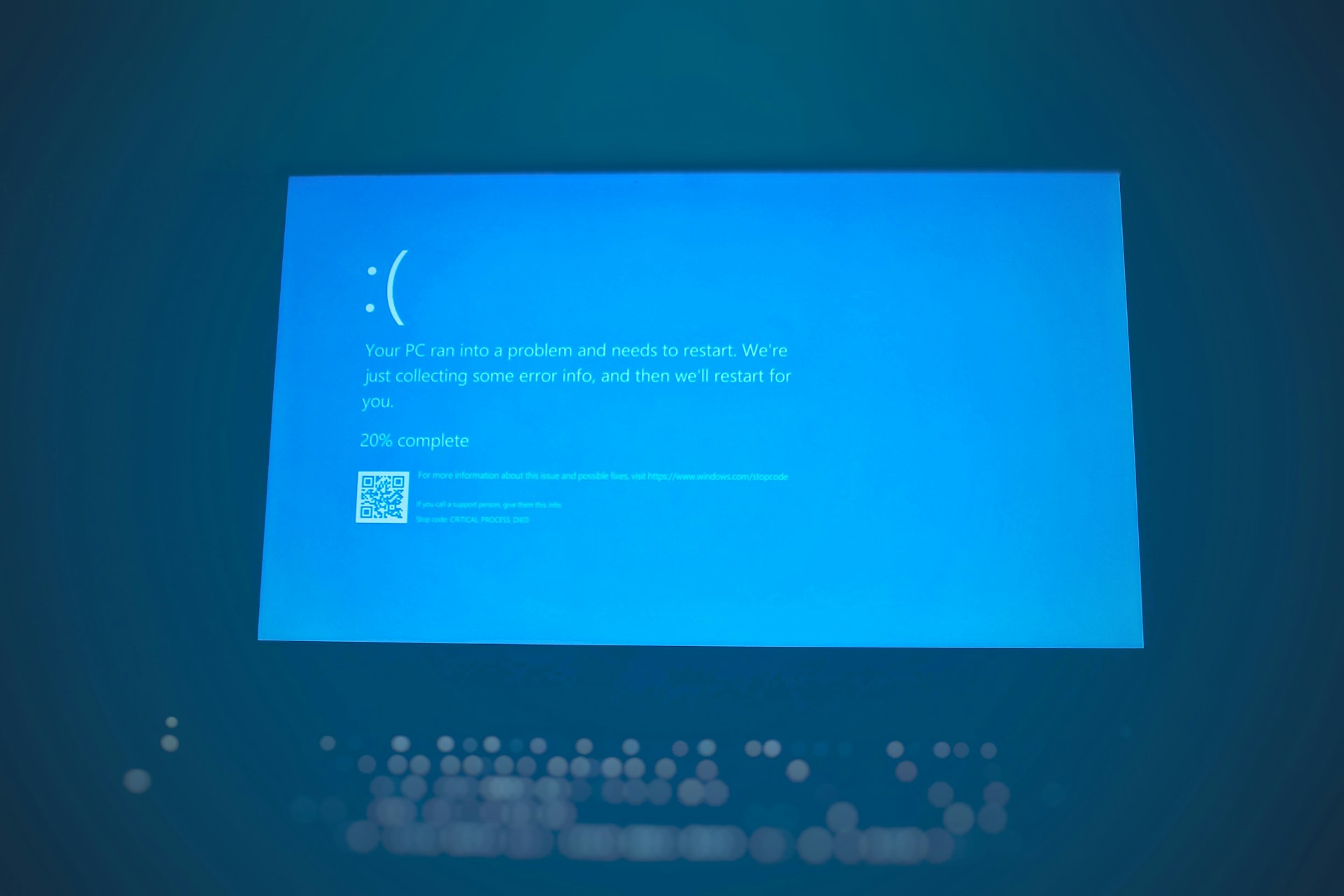
The largest IT outage in history unfolded recently, leaving numerous industries in disarray. Airplanes were grounded, passengers stranded, courts closed, and hospitals reduced to performing only necessary surgeries. Even some news organizations had to improvise to stay on air. This widespread disruption was the result of a software update from cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike, which triggered an error on Microsoft Windows systems, affecting an estimated 8.5 million devices. Notably, Linux and MacOS systems were not impacted.
The chaos that ensued was unprecedented. Airlines lost the ability to check in passengers and luggage, leading to delays and cancellations. Businesses could not operate their cash registers or access electronic files, banks experienced login issues, healthcare providers were unable to check in patients or access their records, and trading on the New York Stock Exchange was delayed at times.
CrowdStrike CEO George Kurtz issued an apology, stating that many companies found that rebooting their systems helped restore service. However, the damage was already done.
As businesses begin to recover and assess the damage, a crucial question arises: What will the impact be on the insurance industry as companies and consumers seek to recover some of their losses from this outage? Although it has not been identified as a cyberattack, cyber coverage could certainly be one of the policies involved.
The Role of Insurance in Mitigating Losses
“The incident outage has the potential to hit several different insurance policies and could go on to become a contract dispute between a corporation and its IT provider,” shares Bernard Regan, a principal with Baker Tilly’s Forensics, Valuation, and Litigation Services practice. “With cyber insurance, there may be cover within these policies related to ‘dependent system outage.’ This effectively means that if you have a third-party providing IT services, and they are affected, then your cyber insurance policy may trigger. If this is the case, then the cyber policy would likely provide cover for costs in relation to data/system restoration and business interruption. If a company could not operate ‘as normal’ and there was a direct causal link to lost revenue or interruption to revenue streams, then a business interruption claim may be forthcoming. However, given some policies have waiting periods, such as eight hours, the incident recovery time will be crucial.”
Meredith Schnur, U.S. & Canada cyber practice leader at Marsh, agrees that cyber claims are likely, as well as claims against other lines. “Cyber insurance policies are the likely place for coverage to be triggered, including business interruption, contingent business interruption, and E&O. Given the magnitude and scope of this outage, we may see consequences that affect product lines beyond cyber risk, most prominently directors & officers (D&O) and property/casualty (P&C).”
Jeffrey Batt, CUO and head of cyber for Pera, a cyber-focused MGA, adds, “Primarily blended cyber/tech E&O policies with dedicated system failure coverage will be impacted. However, depending on how cyber incident triggers are interpreted given relevant policy language, it’s possible that insurers will also see claims notices on dedicated cyber-only policies.”
CrowdStrike themselves might have E&O insurance that may be triggered based on the error that was evident in the released patch, notes Regan. “Currently, the severity of the overall damage/outage caused is unknown, but this is something that the insurance community will be reviewing going forward.”
Other types of policies could come into play and provide some measure of coverage for entities. Loretta Worters, vice president of media relations at the Insurance Information Institute, advises, “Some companies might have Network Downtime Insurance, a parametric solution to protect businesses from losses arising from network service providers such as Microsoft (which was also impacted). Network Downtime Insurance provides coverage for financial losses and other negative impacts following an unexpected interruption to a third-party supplier’s network services. Downtime may be caused by power outages, natural disasters, equipment failure, or any other event that prevents a service from running normally. With parametric insurance, the cover is triggered when the insured’s cloud is down for a period specified in the policy, usually with a time-based deductible, sometimes after an hour.”
Vulnerability to Cyberattacks
The outage also left businesses utilizing CrowdStrike’s software vulnerable to cyberattacks. “This outage can cause major cyber incidents. If networks are down and needing reboots or businesses are receiving phishing emails from domains including CrowdStrike, individuals and businesses may be vulnerable and open to cyberattacks, malware, etc.,” says Tony Abrudeanu, RPLU, vice president, executive lines practice leader for DOXA Insurance Programs. “For example, there are already many domains being purchased shortly after the outage referencing the name CrowdStrike. This is being used for phishing emails/attacks. This would trigger cyber policies.”
Douglas Wells, director at Sedgwick, Forensic Accounting Services, provides some insight into how cyber coverage and some exclusions could be viewed. “While cyber policies typically cover malicious acts, many of them also include coverage for human error leading to IT infrastructure failure and events of that nature. Policies also commonly cover contingent business interruption to insureds where their service provider has been subject to a breach, human error, or IT failure. This occupies a narrow lane that a primary cyber policy would respond to a first-party claim.”
“Given this was not a reported cyberattack, coverage will likely depend on the wording of cyber policies to see how computer systems have been defined,” explains Regan. “If any externally connected devices or networked environments are considered as part of the corporate network, this may represent a covered loss. However, if there is an exclusion stating all systems outside of the network are considered as third-party, any outage of those services may not be covered. In addition, the definition of ‘Outsourced Service Provider’ may also be relevant given how CrowdStrike is likely to have operated with their clients.
Alternatively, some insurance carriers may consider this type of incident as a ‘system failure’ event which is not covered under all policy forms that exist in the cyber insurance market.”
Batt finds that “the intent of most dedicated cyber-only policies is to exclude cyber incidents and events that are not related to unauthorized data use or access. However, if some policies are not explicit around this definition or wording, despite the carrier’s actual intent, it could be arguable that the scope of such coverage is broader and includes cover for system failure and IT-related outages.”
Impact on the Travel Industry
The impact on the travel industry was apparent almost immediately, as more than 3,400 flights were canceled initially because of the outage, according to FlightAware, with Delta Airlines being one of the most affected carriers. Spirit, United, and American flights were also canceled or extremely delayed.
As unhappy travelers missed or had to defer their vacations, airlines were overwhelmed as they tried to reticket or rebook customers. The value of travel insurance became much more apparent as weary travelers had to stay at or near airports, pay for extra meals, or even buy clean clothes when their luggage was unavailable. “The Federal Government, including the Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg, have directed travelers to the Airline Passengers’ Bill of Rights,” says Timothy Wirth, executive general adjuster at Sedgwick. “Those with travel insurance should explore their options and review the conditions and coverage of their policy.”
Current Status
Travel is still disrupted several days later and many of the claims related to the outage are just beginning. The next installment of this series will examine the opportunities for subrogating some of these claims, the legal implications for some of the parties involved, and what lessons can be learned for carriers and customers alike.
Related posts

Starting a Managing General Agency (MGA) can be both thrilling and overwhelming. You’ve got the vision. You know the market need. But translating that into a functioning insurance entity—with...
Continue Reading
In today’s increasingly digitized world, the U.S. Marine Transportation System (MTS) stands as a vital artery of global commerce, quietly powering trillions in annual trade. But as this ecosystem...
Continue Reading